Calcium Hydroxyapatite’s Effect on Bone Mineral Density
Bone mineral density (BMD) is a critical indicator of bone strength and an essential factor in preventing osteoporosis and fractures, especially in aging populations. While calcium supplementation is a common approach to maintaining bone health, not all forms of calcium are equally effective. Among the various options, calcium hydroxyapatite has emerged as a superior form, offering unique advantages for improving and maintaining bone mineral density.
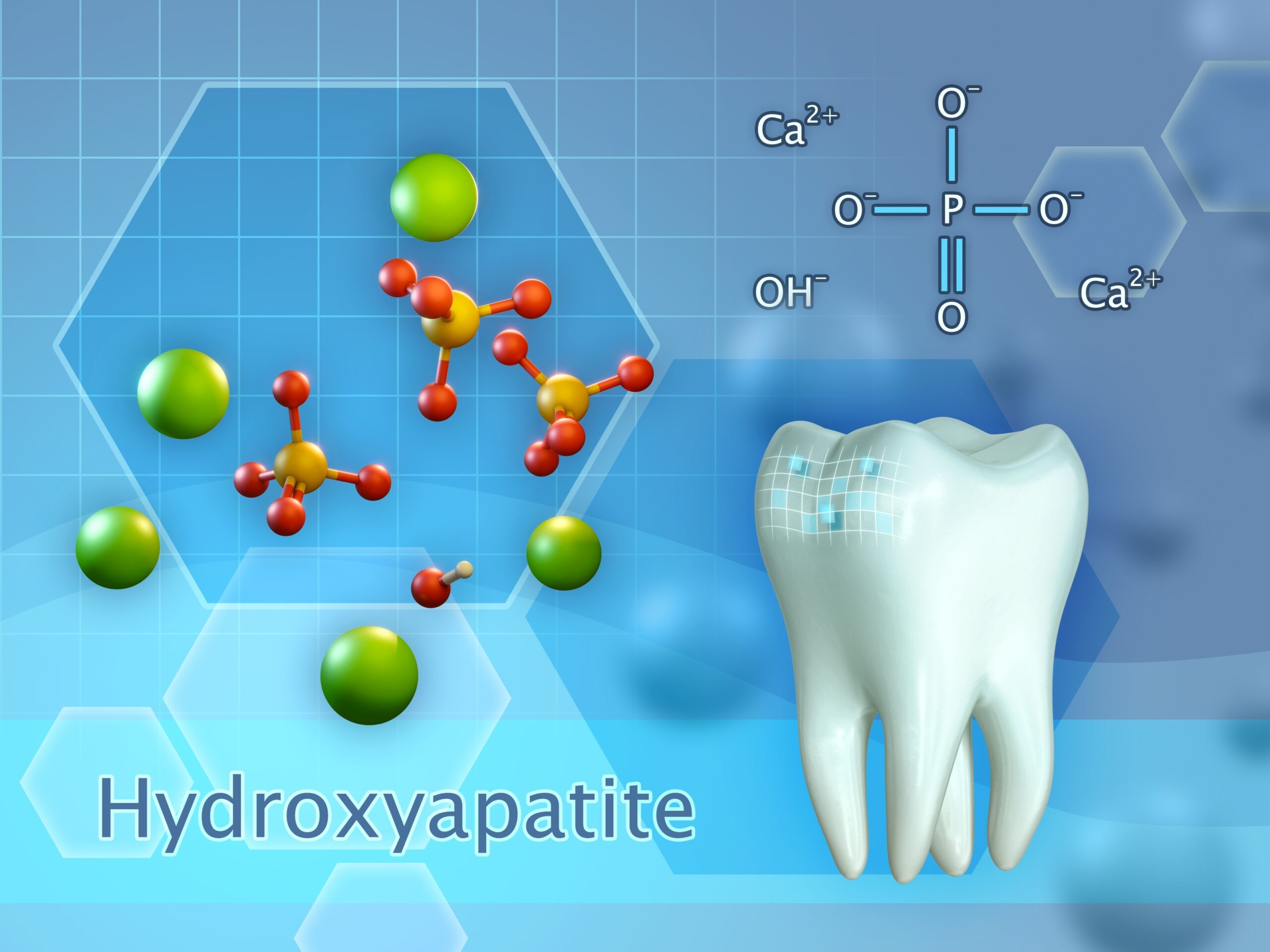
What Is Calcium Hydroxyapatite?
Calcium hydroxyapatite (Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2) is the naturally occurring mineral form of calcium found in human bones and teeth. Unlike conventional calcium supplements such as calcium carbonate or calcium citrate, calcium hydroxyapatite is a whole bone extract that contains:
- Calcium
- Phosphorus (in an ideal 2:1 ratio)
- Type I collagen
- Trace minerals like magnesium, zinc, and boron
- Bone growth factors and proteins
This complex composition closely resembles the natural structure of human bone, which may contribute to its effectiveness in promoting bone regeneration and strength.
How Calcium Hydroxyapatite Affects Bone Mineral Density
1. Superior Bioavailability and Retention
Calcium hydroxyapatite is more than just a source of elemental calcium. Its microcrystalline form enhances bioavailability, allowing it to be more readily absorbed and retained in bone tissue. This means more of the calcium you consume actually reaches the bones where it is needed.
2. Supports Both the Mineral and Collagen Matrix
Bones are made up of a mineral phase (mostly hydroxyapatite) and a protein matrix (largely collagen). Traditional calcium supplements provide only minerals, but calcium hydroxyapatite also supports the collagen framework, which plays a crucial role in bone flexibility and resistance to fractures.
3. Reduces Bone Resorption
Some research suggests that calcium hydroxyapatite can help inhibit the activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone breakdown. This contributes to a more favorable balance between bone formation and resorption, helping to preserve or improve bone density over time.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Its Use
A growing body of research supports the beneficial effects of calcium hydroxyapatite on BMD:
- A landmark study published in Calcified Tissue International (1995) compared calcium hydroxyapatite to calcium carbonate in postmenopausal women. The group receiving hydroxyapatite had significantly better maintenance of BMD over a two-year period.
- A 2007 randomized clinical trial found that women taking calcium hydroxyapatite supplements had greater improvements in spinal BMD compared to those taking calcium carbonate, even when total calcium intake was the same.
- Meta-analyses have indicated that calcium hydroxyapatite may not only prevent bone loss but also reduce the risk of fractures, particularly in individuals with osteopenia or osteoporosis.
Key Nutritional Synergies
For optimal results, calcium hydroxyapatite should be taken as part of a comprehensive bone health protocol that includes:
- Vitamin D3 – Enhances calcium absorption in the gut.
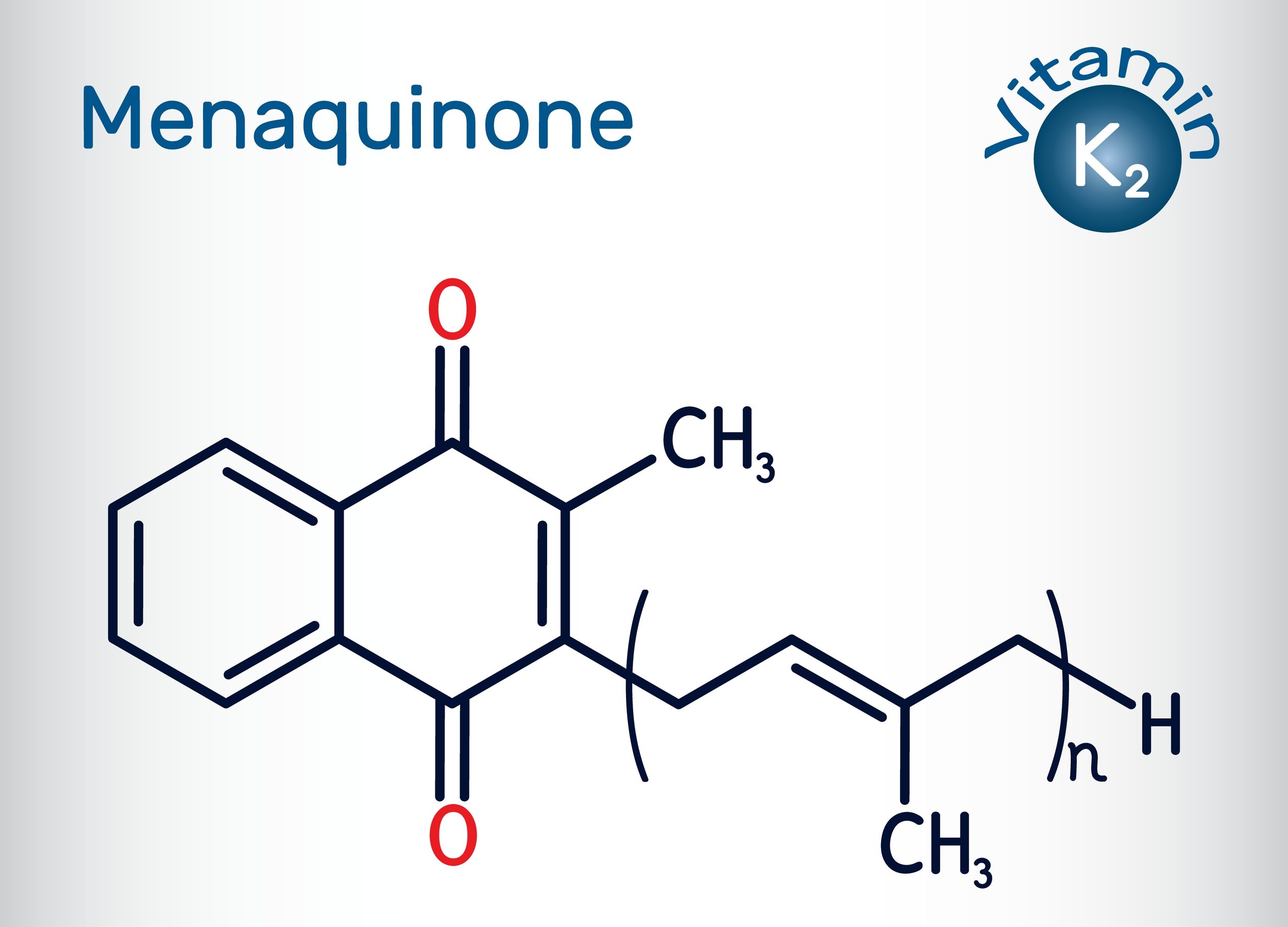
- Vitamin K2 (MK-4 or MK-7) – Directs calcium to the bones and prevents arterial calcification.
- Magnesium – Essential for proper calcium metabolism.
- Boron and zinc – Support bone matrix formation and hormone balance.
These nutrients work synergistically to ensure that calcium is effectively absorbed, utilized, and incorporated into bone tissue.
Safety and Considerations
When used properly, calcium hydroxyapatite is generally considered safe and well-tolerated. However, excessive calcium intake from any source may contribute to kidney stones or vascular calcification, especially when not balanced with vitamin K2 and magnesium. Individuals with pre-existing kidney or cardiovascular conditions should consult a healthcare provider before beginning supplementation.
Look for microcrystalline hydroxyapatite (MCHC) sourced from grass-fed, antibiotic-free, BSE-free cattle to ensure purity and safety.
Conclusion
Calcium hydroxyapatite offers a highly effective, bone-friendly form of calcium that mirrors the structure of human bone. Unlike standard calcium supplements, it supports not just the mineral content of bones but also the underlying protein matrix, making it a superior option for improving and maintaining bone mineral density. For individuals looking to enhance skeletal strength, prevent fractures, or manage osteoporosis naturally, calcium hydroxyapatite represents a clinically supported and biologically compatible solution.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement protocol.